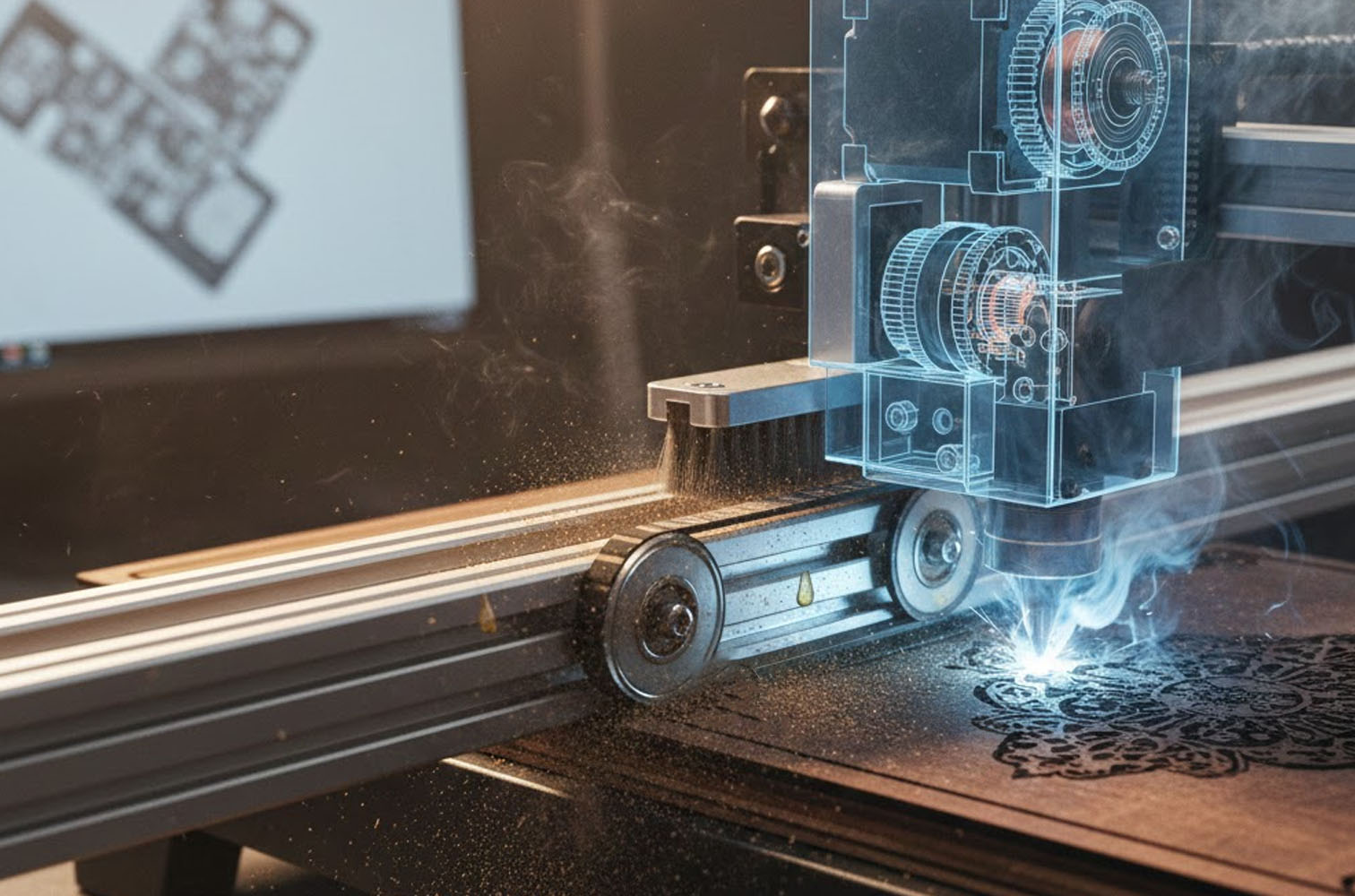
Red vs. Blue: Navigating the spectrum of diode laser engraving
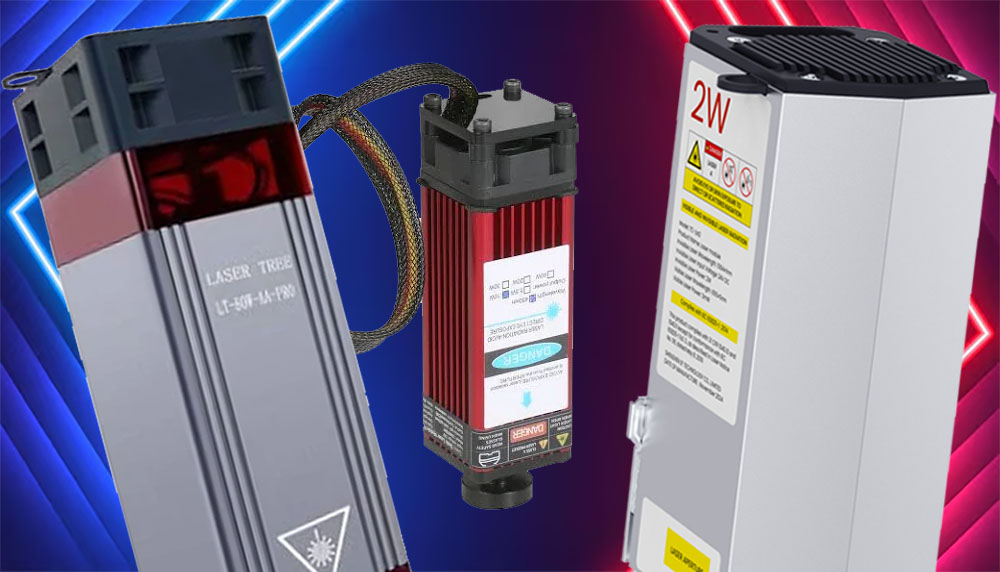
Diode lasers have revolutionised the world of engraving, offering accessible and versatile tools for hobbyists and professionals alike. However, not all diode lasers are created equal. One key distinction lies in their emitted wavelength, primarily categorised as red or blue.
Understanding the differences between these laser types is crucial for optimising your engraving results.
The wavelength divide:
Blue diode lasers, typically operating around 445-450nm, are the most common in consumer-grade engravers. They offer a good balance of power and versatility, excelling at engraving and cutting a wide range of materials. Red diode lasers, usually around 635-660nm, are less prevalent but offer unique advantages for specific applications.
Blue lasers: The versatile workhorse:
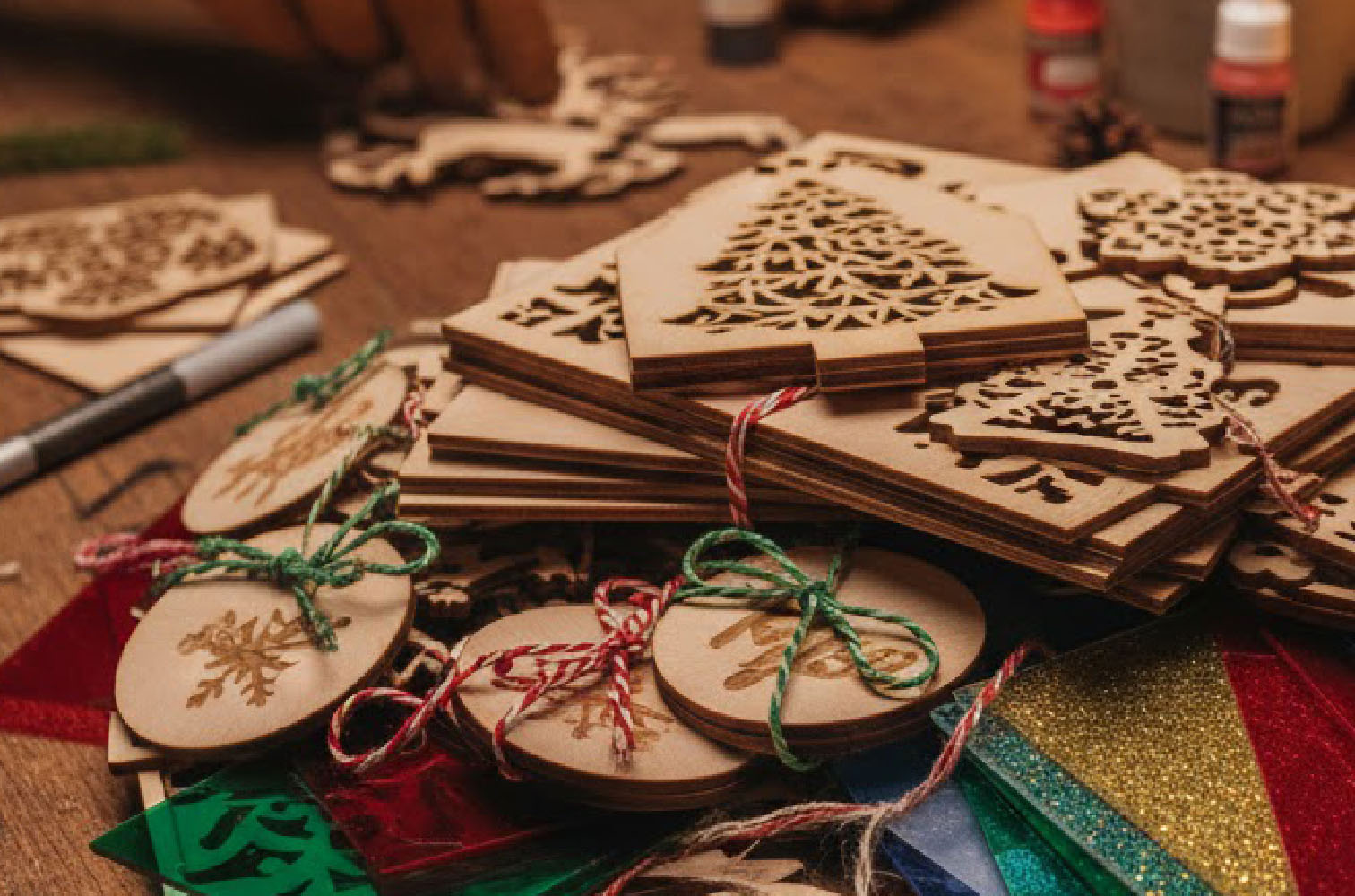
Blue lasers are highly effective on materials that absorb blue light well. This includes wood, acrylic, leather, and dark-colored materials. Their higher energy density allows for faster cutting speeds and deeper engravings. They are the go-to choice for general-purpose engraving and cutting tasks.
Best for:
- Wood engraving and cutting
- Acrylic engraving and cutting (excluding blue acrylic)
- Leather engraving
- Dark-colored materials
- Detailed image engraving
Red lasers: The specialised tool:
Red lasers are more readily absorbed by certain materials, particularly those with a higher reflectivity in the blue light spectrum. This makes them ideal for engraving metals and some lighter-colored materials. They also produce a finer dot, leading to very high detail engravings.
Best for:
- Engraving certain metals (depending on reflectivity)
- Light-coloured materials
- very highly detailed image engravings.
- Red Lasers and Cutting Limitations:
Red diode lasers are generally less effective at cutting compared to blue lasers of the same power. The longer wavelength carries less energy, requiring slower speeds and multiple passes to cut through materials. This limits their practicality for cutting thicker materials.
Tips for Optimal Results:
Blue Lasers:
- For acrylic, avoid blue hues as they reflect the laser.
- Use air assist to minimise charring and improve cut quality.
- Experiment with power and speed settings to find the optimal parameters for each material.
Red Lasers:
- Test on scrap material to determine compatibility with metals.
- Use proper safety glasses designed for the specific red wavelength.
- Focus carefully, the finer dot means focus is more important.
In summary, blue lasers offer greater versatility for general-purpose engraving and cutting, while red lasers excel in specialised applications like metal engraving and very high detail engravings. Understanding the unique characteristics of each laser type allows you to select the best tool for your specific needs.

Editor at TopEngravers. Specialising in reviews of new laser engraving products, practical engraving tips, and detailed engraver guides.